Construction Site Digitalization: Preparing for the Future
The construction industry is one of the world’s largest employers, yet for decades it has lagged behind other sectors in terms of efficiency and cost control. Increasing global competition, sustainability demands, and rapidly evolving technologies are now pushing the industry toward digital transformation.
Today, digitalization is no longer a “future ambition” but a necessity for achieving efficiency, transparency, and sustainability on construction sites.

Key Benefits of Digitalization
1. Time and Cost Savings
Planning errors, delayed starts, and rework often lead to wasted time and unexpected costs.
-
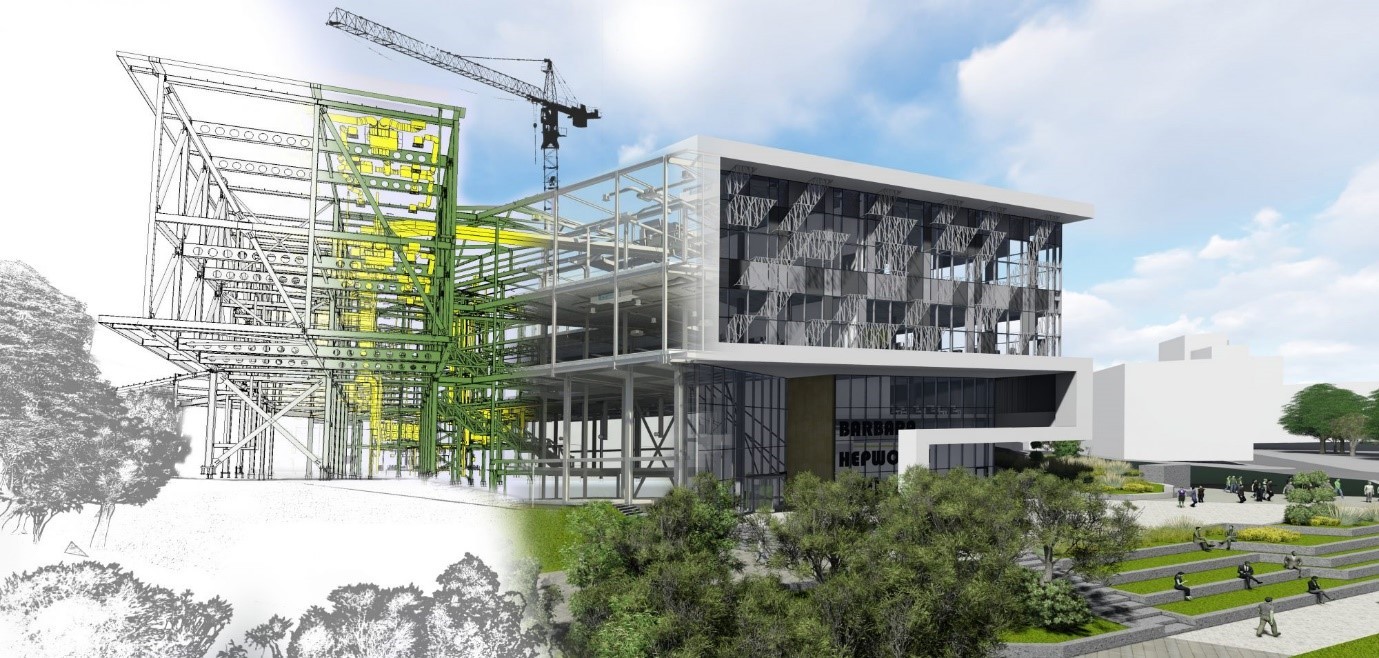
Digital twins and 4D/5D BIM applications help identify these risks early.
-
As a result, projects benefit from more accurate budgets and reliable schedules.
2. Transparency
In traditional workflows, data is often lost between contractors, subcontractors, and offices.
-
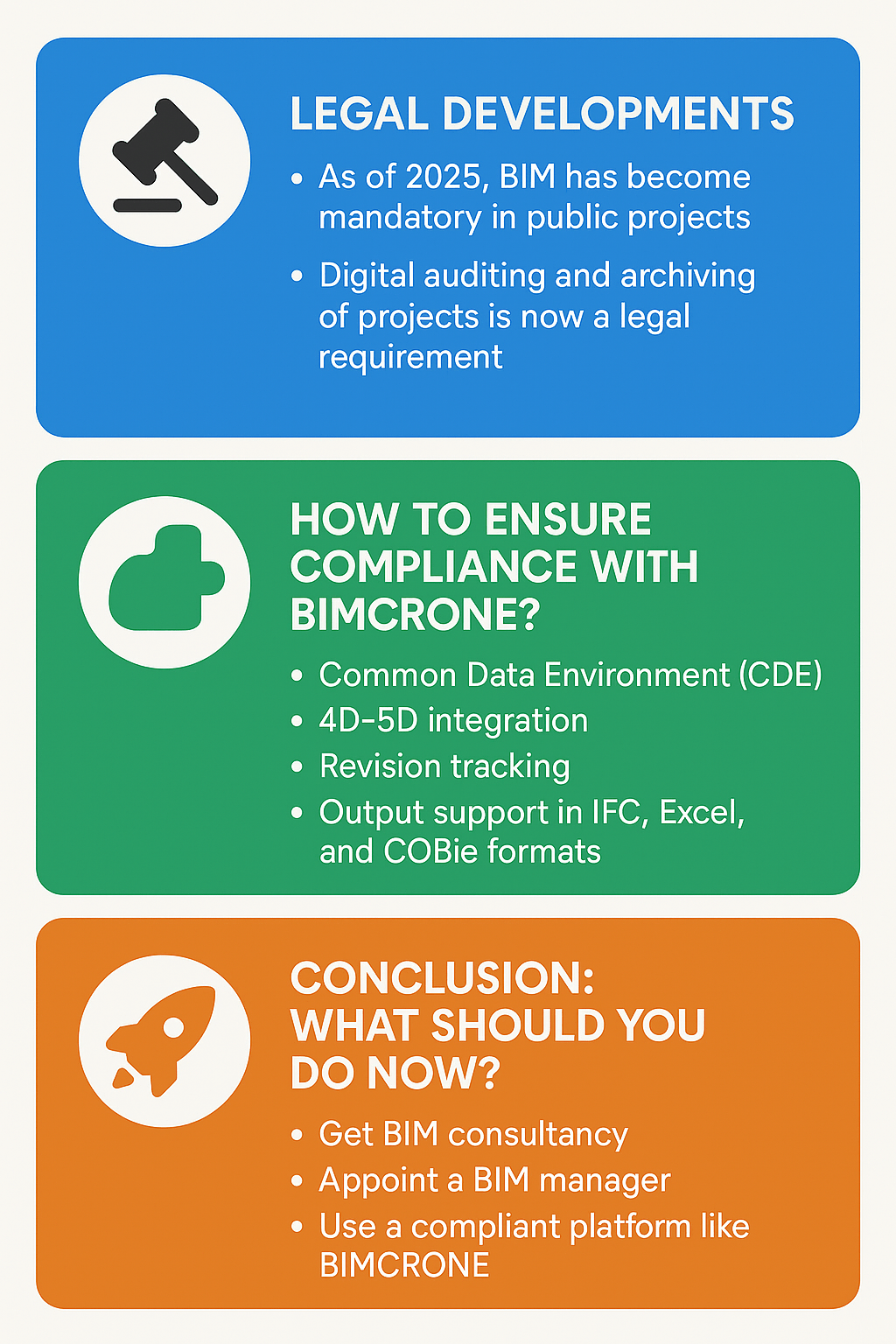
A Common Data Environment (CDE) ensures that all stakeholders—contractors, subcontractors, clients, and technical teams—access the same source of information.
-
This minimizes misunderstandings and data loss significantly.
3. Quality and Compliance
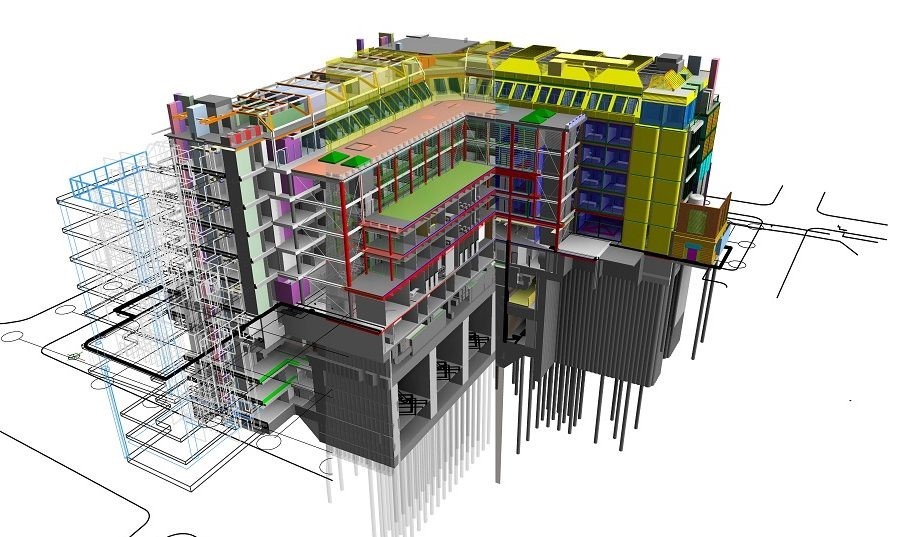
Model-based quality control, continuous revision analysis, and legal compliance guarantee project reliability at every stage.
-
Compliance with national and international standards (IFC, COBie, LOD, etc.) also becomes much easier with digital processes.
4. Sustainability
Energy simulations, material optimization, and waste management are some of the critical advantages digitalization brings.
-
This delivers not only environmental benefits but also economic value.
Key Elements for Successful Digitalization
-
Common Data Environment (CDE): A single source of truth for all project data
-
3D/4D/5D BIM Models: Beyond visuals—supporting time, cost, and quality management
-
Real-Time Tracking & Reporting: Early detection of delays and performance insights
-
Legal Compliance & Standards: Ensuring adherence to IFC, COBie, LOD, and local regulations
-
Team Training & Cultural Change: Encouraging site and office teams to embrace digital tools
Conclusion
Digitalizing construction sites is no longer just a competitive advantage—it’s a requirement for survival in today’s industry.
-
Model-based project management,
-
real-time monitoring,
-
common data environments, and
-
sustainability-driven solutions
are enabling construction projects to achieve higher efficiency, improved quality, and long-term value.
With digital transformation, the construction industry is steadily moving toward a more transparent, cost-effective, and sustainable future.